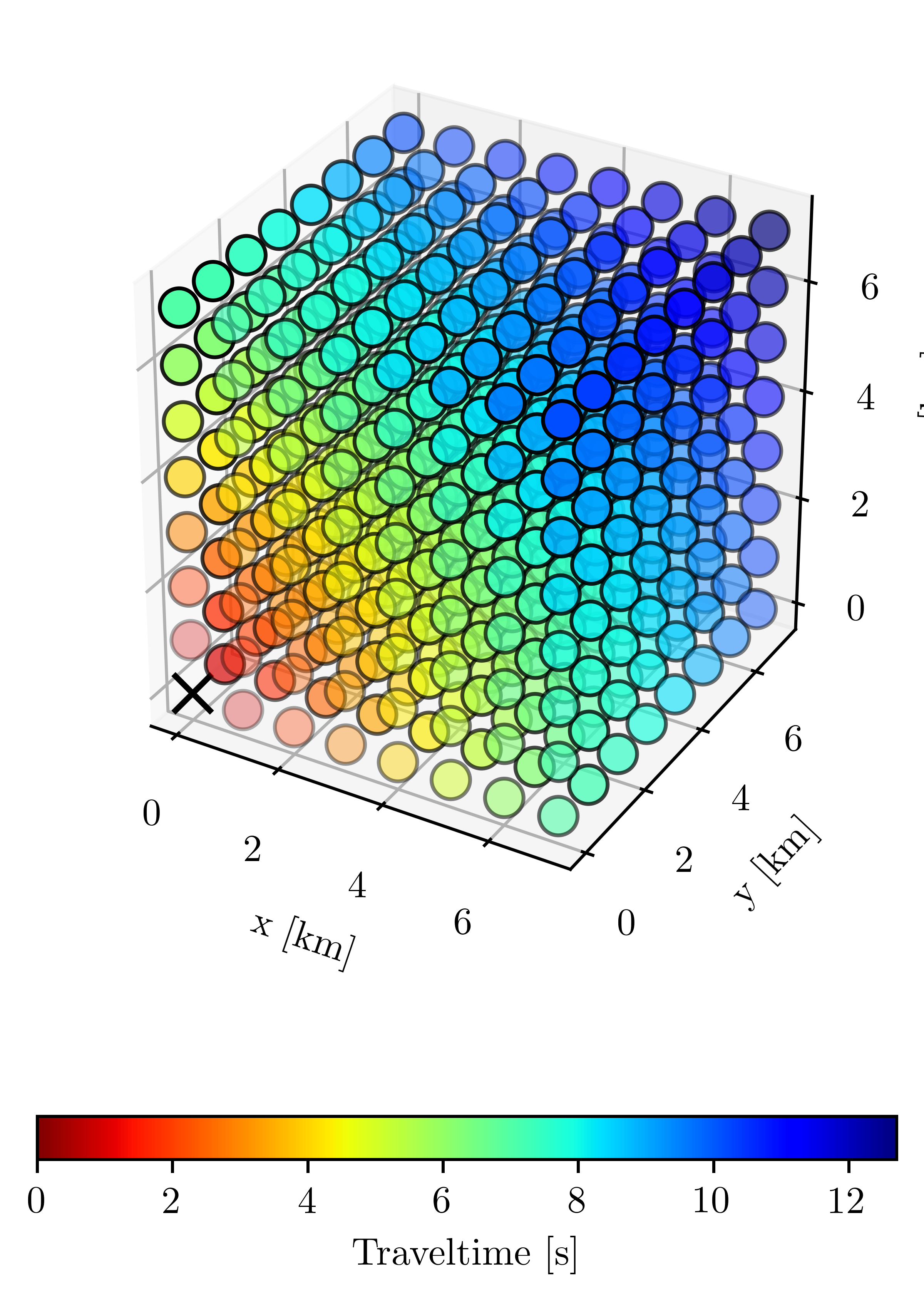
Cartesian 3D¶
Identical to the Cartesian 2D example except this time extend the computational grid by 8 nodes in the z direction.
import numpy as np
import pykonal
# Initialize the solver.
solver = pykonal.EikonalSolver(coord_sys="cartesian")
solver.velocity.min_coords = 0, 0, 0
solver.velocity.node_intervals = 1, 1, 1
# This time we want a 3D computational grid, so set the number of grid nodes
# in the z direction to 8 as well.
solver.velocity.npts = 8, 8, 8
solver.velocity.values = np.ones(solver.velocity.npts)
# Initialize the source.
src_idx = 0, 0, 0
solver.traveltime.values[src_idx] = 0
solver.unknown[src_idx] = False
solver.trial.push(*src_idx)
# Solve the system.
solver.solve()